PART A:
In this unit, we learned about different way of moving, not transportation wise, but moving up, down, at an angle, etc.
Newton's Second Law --
In this lesson of the unit, I learned that things are able to accelerate and the cause of acceleration is force. This is because force is proportional to acceleration.
For instance, if force increases, acceleration will too and vise versa.
That can be represented as a~F
This formula also means that acceleration is directly proportionate to force and it is inversely proportional to mass.
Analyzing this further, a larger mass will mean that there is a small acceleration.
Another part of this law has to do with mass and weight. This now includes things falling, not just moving to the left or the right, therefore we have to acknowledge gravity.
A formula for this is: weight = mass times gravity or w=mg. We learned that gravity will always be 9.8m/s, or to make things easier, round it up to 10m/s.
For example: If a box has a mass of 2kg and we know that gravity is 10m/s, what is the weight?
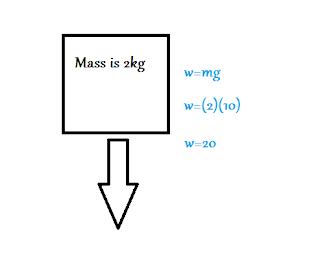 |
| Looking at this example, this is how you would solve |
We learned that if the net force is constant, acceleration is constant also. To find the force of the system, we use the equation shown above w=mg. To find the mass of a system, we simply just add the weight of the items used.
Skydiving --
In the skydiving lesson, we learned that as speed increases, the force of air resistance increases. In simpler terms,they are directly proportional.
REMEMBER: this is in terms that you are accelerating on earth only.
This also means that you start out at zero seconds.
An easy way to think about this is to remember that f.net = f.weight - f.air
Also, if net force decreases, acceleration decreases because they are directly proportional, in this case. In terms of the velocity, it always increases because it is still accelerating.
| F.grav can also be seen as f.weight |
Two things that will change air resistance, are speed and surface area. This is because they are both proportionate to air resistance.
 |
| This is showing terminal velocity; the point in which both the f.weight and f.air are equal |
As much as the arrows in both of these images want to make you think that the person is moving upward, remember that it is not. It never moves upward. All it is trying to show is how it is attempting to reach terminal velocity.
So all in all, when your speed goes up, your air resistance does too.
Also, a key point while learning about physics is that a negative sign does not mean negative, it means that it is going in the opposite direction. Now look at the pictures below, and try to solve for each one. The answers are included below.
Free Fallin' --
In free fall, there are many things to remember:
- There is no air resistance
- The only force acting on it is gravity
- It is at a constant 10m/s
- It does not matter what the weight of the objects are, gravity is the only thing that matters and like I stated before, it is 10m/s^2
This is how you know that it is due to gravity alone:
 |
| Created on Paint |
Someone was on top of a cliff. They threw a ball straight down. It took 3 seconds to hit the ground.
- How high is the building/How far in 3s:
- d=1/2gt^2
- d=1/2(10)(3)^2
- d=1/2(10)(9)
- d=1/2(90)
- d=45 m
- How fast did the ball go?
- v=gt
- v=(10)(3)
- v=30 m/s
Projectile Motion --
When something is moving in two directions. We have to figure out the vertical and horizontal directions.
1. Vertical Direction: has a constant acceleration (10m/s). We use the formula d=1/2gt^2. Vertical velocity is basically the height, and the height determines time.
2. Horizontal Direction: always remains with a constant velocity because it has no force. We can calculate horizontal velocity by using the formula v=d/t.
Projectile motion follows a parabolic path.
Throwing Things up at an Angle--
In conceptual physics, we will always throw things at a 45 degree angle. When we throw something, it is moving in the horizontal direction to reach its end point. The vertical velocity will be the height and something we will always know is that it has a constant velocity.
In order to find the horizontal velocity, we use the same equation as before v=d/t. But when throwing things at an angle, we have to use the equation a²+b²=c²| As you can tell, the horizontal velocity always remains constant, and the vertical increases |
In order to find the hang time of the object, you do the same thing you've done with everything else. You must start from the initial velocity and decrease by 10m/s going up, and going down you must increase.
| A real life example of throwing things at an angle |
- In this unit, I found that it took me a long time to grasp the concepts. Throwing things straight up is still a lesson that I have not yet grasped completely.
- I overcame this difficulty by going into conference period well before the test in order to study more. Also I re watched the video and looked at the lesson in the book.
- I wouldn't say the light bulb has necessarily clicked yet, but what has made it clearer is that I have used multiple resources in order to learn more.
**My problem-solving skills, effort, and learning**
In this unit, I feel like I showed effort even when I didn't understand (which was most of the time). I did not get frustrated or lose my patience even when other people were being distracting. I completed all of my homework for this unit an came into conference period. In the class, I showed up on time with my homework done and questions ready. With the blog posts, I always posted them before the class periods and I found helpful videos again.
- Persistence: I am usually always determined to get the answers correct and to master the lesson day by day. Although that has not happened much in this unit, I feel like I was still persistent in trying to learn the lessons.
- Communicating both spoken and written words: In class, I do not feel like I participate as much as I should. I think my written work is better than my oral skills.
- Collaboration with group members: My podcast group is perfect, therefore it is really easy to each take a part and do what we have to do, which I think I collaborate a lot in. In my labs, however, it is usually hard to stay focused but I usually collaborate a lot on these because if I dont, we wont get it done, which at times is frustrating.
GOAL: Next time, I hope to speak up a little more when I don't understand something, even if the class may get annoyed.
PART B:
I learned in this unit, that we can apply Newton's second law to things that have direction such as up, down, at an angle etc. I like using real world examples in order to grasp the material a little more. I can relate throwing things down to a ball for example. I can connect throwing things at an angle to kicking a soccer ball.
HERE IS THE PODCAST FOR THIS UNIT: Created by Jasmin, Catherine Eckerd, and Abby.
According to Ms. Lawrence, it was really well done, so watch it! You might learn something! Enjoy!

